
In today’s complex landscape of federal project management, the creation of a Project Management Office (PMO) stands as a cornerstone of strategic success. This comprehensive guide delves into the crucial role of PMOs in enhancing efficiency, ensuring compliance, and fostering consistent, high-quality outcomes within federal agencies.
With a unique blend of challenges inherent to federal projects, ranging from intricate regulatory demands to the need for meticulous planning and execution, establishing a PMO is more than a necessity—it’s a transformative step towards achieving organizational excellence. As we embark on this journey, we’ll explore the intricacies of setting up a PMO tailored to the federal context, offering insights into the planning, implementation, and continuous improvement phases that underpin a successful PMO in the heart of government operations.
Understanding the PMO in the Federal Context
Federal agencies’ Project Management Offices (PMOs) are crucial hubs for overseeing, organizing, and implementing projects. They act as centralized units responsible for standardizing project management practices, ensuring compliance, and fostering consistency across various initiatives within the government sphere.

Definition and Role of a PMO in the Context of Federal Agencies
In a federal agency context, a PMO orchestrates project-related activities, offering strategic guidance, governance, and support. It acts as a cornerstone in aligning project execution with broader agency objectives. This involves defining standardized methodologies, tools, and best practices, providing a structured framework for efficient project management.
The Significance of Centralized Project Management in Government Projects
Centralized project management through a PMO is critical for government projects due to their complexity and scale. Federal agencies often handle multifaceted projects that require meticulous planning, stringent oversight, and adherence to regulatory requirements.
A PMO streamlines these efforts by establishing uniform processes, improving collaboration, and mitigating risks inherent in large-scale government endeavors.
Benefits of Establishing a PMO in a Federal Agency Context
The establishment of a PMO within federal agencies brings forth numerous advantages. It promotes consistency in project execution, leading to better resource allocation, reduced redundancy, and improved project success rates.
Furthermore, it enhances transparency, fosters accountability, and improves decision-making through data-driven insights.
Planning Phase: Setting Up the PMO
The planning phase is the first step in setting up a Project Management Office (PMO) for federal agencies. This phase involves assessing the agency’s project management needs and goals, identifying key stakeholders and their roles in the PMO, and creating a roadmap and strategy for PMO implementation.
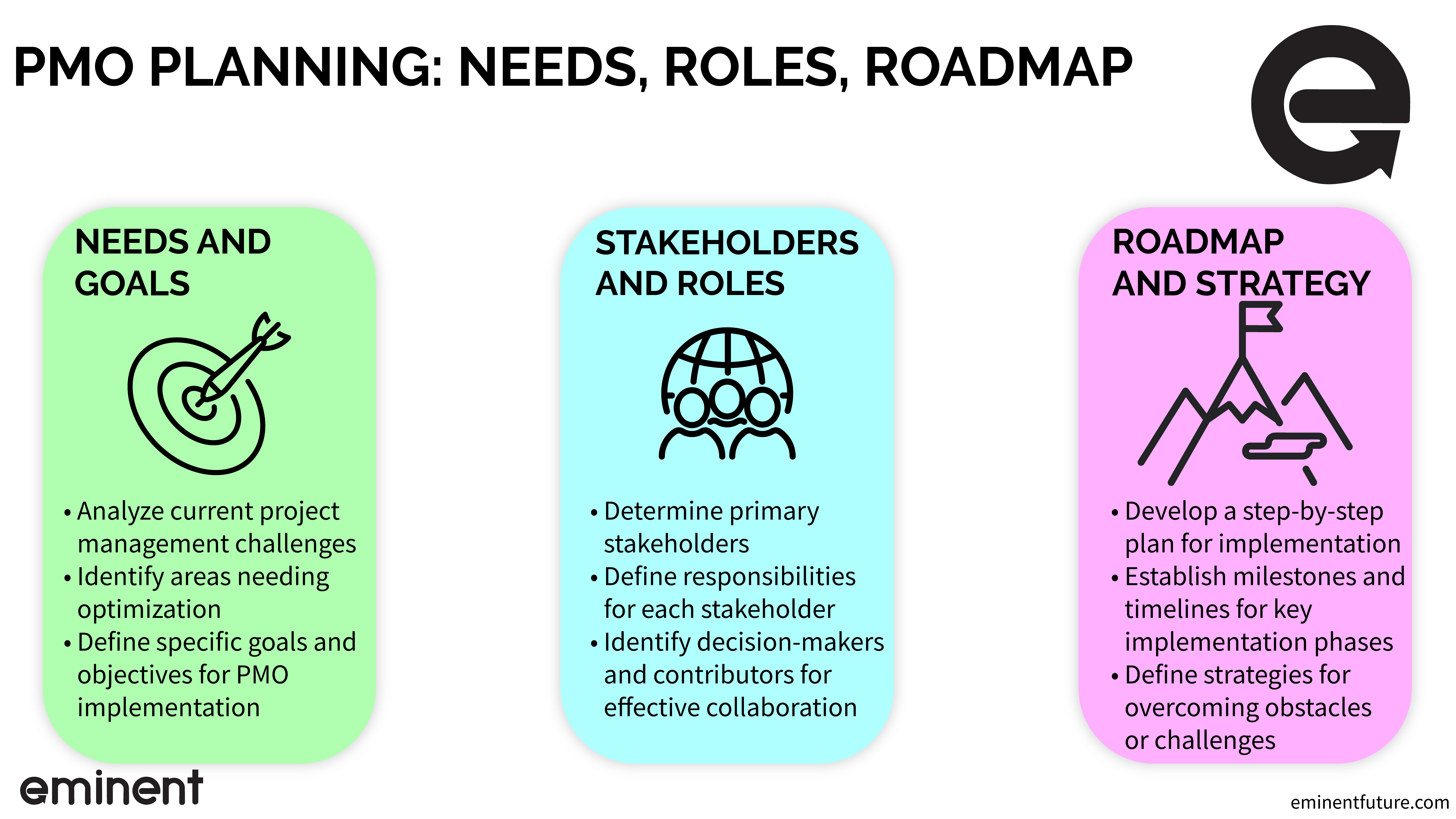
Assessing the Agency’s Project Management Needs and Goals
The first step in the planning phase is to assess the agency’s project management needs and goals. This involves identifying the agency’s current project management practices, processes, tools, and any gaps or areas for improvement. The assessment should also consider the agency’s strategic goals and objectives and how project management can support these goals.
Identifying Key Stakeholders and Their Roles in the PMO
The next step is identifying key stakeholders and their roles in the PMO. This includes identifying the PMO sponsor, who will provide the necessary support and resources for the PMO, and the PMO manager, who will be responsible for the day-to-day operations of the PMO. Other key stakeholders may include project managers, business analysts, and subject matter experts.
Creating a Roadmap and Strategy for PMO Implementation
The final step in the planning phase is to create a roadmap and strategy for PMO implementation. This involves developing a detailed plan for implementing the PMO, including timelines, milestones, and deliverables. The roadmap should also identify any risks or challenges during implementation and how these will be addressed.
PMO Framework Tailored for Federal Projects
The PMO framework tailored for federal projects is a crucial aspect of the planning phase. This framework involves adapting industry-standard PMO frameworks for federal projects, addressing compliance, regulations, and security considerations unique to federal agencies, and outlining the structure and governance model of the federal agency’s PMO.
Adapting Industry-Standard PMO Frameworks for Federal Projects
Adapting industry-standard PMO frameworks for federal projects involves tailoring existing PMO frameworks to meet the specific needs of federal agencies. This includes identifying the unique requirements of federal projects, such as compliance, regulations, and security considerations, and incorporating these requirements into the PMO framework.
Addressing Compliance, Regulations, and Security Considerations Unique to Federal Agencies
Federal agencies are subject to various compliance, regulations, and security considerations unique to the public sector. These considerations must be addressed in the PMO framework to ensure that the PMO is aligned with the agency’s goals and objectives while also meeting the requirements of federal regulations.
Outlining the Structure and Governance Model of the Federal Agency’s PMO
The structure and governance model of the federal agency’s PMO should be outlined in the PMO framework. This includes identifying the roles and responsibilities of the PMO sponsor, PMO manager, and other key stakeholders, as well as the reporting structure and decision-making processes within the PMO.
PMO Framework Tailored for Federal Projects
The Project Management Office (PMO) framework is essential to any project management system. It provides a structured approach to managing projects, ensuring they are delivered on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards. However, the PMO framework must be tailored to meet the specific needs of federal projects. This section outlines the key considerations when adapting industry-standard PMO frameworks for federal projects.

Adapting industry-standard PMO frameworks for federal projects
The first step in developing a PMO framework tailored for federal projects is to adapt industry-standard PMO frameworks to meet the unique requirements of federal agencies. This involves identifying the key differences between federal and non-federal projects and modifying the PMO framework accordingly.
For example, federal projects are subject to a range of compliance, regulatory, and security considerations that are not present in non-federal projects. As such, the PMO framework must be adapted to address these unique requirements.
Addressing compliance, regulations, and security considerations unique to federal agencies
Compliance, regulatory, and security considerations are critical to any federal project. As such, the PMO framework must be designed to address these unique requirements.
This involves developing policies and procedures that ensure compliance with federal regulations and implementing security measures that protect sensitive information. The PMO framework must also be designed to provide the relevant rules and standards to deliver all projects.
Outlining the structure and governance model of the federal agency’s PMO
The structure and governance model of the federal agency’s PMO is a critical component of the PMO framework. It defines the roles and responsibilities of the PMO team, as well as the processes and procedures that govern the management of projects.
The structure and governance model must be designed to ensure the PMO team has the resources and authority to manage projects effectively. It must also be prepared to ensure that the PMO team is accountable for the delivery of projects and that there is clear communication between the PMO team and other stakeholders.
Tools and Technology for Federal PMOs
The success of a Project Management Office (PMO) depends on the tools and technology it uses to manage projects. However, selecting the right tools and technology for a federal PMO can be challenging. This section outlines the key considerations when identifying project management tools suitable for federal agency environments.

Identifying project management tools suitable for federal agency environments
When selecting project management tools for federal agencies, it is vital to consider the unique requirements of these environments. Federal agencies are subject to various compliance, regulatory, and security considerations not present in non-federal environments. Project management tools must be selected with these unique requirements in mind. Some popular project management tools suitable for federal agency environments include:
- Microsoft Project: A project management software that provides tools for planning, scheduling, and tracking projects. It is compliant with federal security and data protocols. FedRAMP certified.
- Smartsheet: A cloud-based project management tool that provides tools for project planning, tracking, and collaboration. It is compliant with federal security and data protocols. FedRAMP certified.
Platforms compliant with federal security and data protocols
Federal agencies are subject to strict security and data protocols. As such, selecting project management tools compliant with these protocols is crucial. Some popular project management software and platforms that are compliant with federal security and data protocols include:
- Microsoft Teams: A collaboration platform that provides tools for chat, video conferencing, and file sharing. FedRAMP certified.
- Google Workspace: A cloud-based productivity suite that provides email, document creation, and file-sharing tools. FedRAMP certified.
- Salesforce: A cloud-based customer relationship management (CRM) software that provides tools for managing customer interactions and data. FedRAMP certified.
integration of tools within existing agency infrastructure
When selecting project management tools for federal agencies, it is essential to consider the existing agency infrastructure. To ensure effectiveness, project management tools must be integrated with existing systems and processes. Some popular project management tools that can be combined with existing agency infrastructure include:
- Microsoft Power Platform: A low-code platform that provides tools for building custom applications and automating workflows that can be integrated with existing Microsoft systems and processes. FedRAMP certified.
- ServiceNow: A cloud-based platform that provides tools for IT service management, operations management, and business management. It can be integrated with existing systems and processes. FedRAMP certified.
- Jira: A web-based project management tool that provides tools for issue tracking, project management, and software development. It can be integrated with existing systems and processes. *(In the process of gaining FedRAMP certification as of DEC 23)
Talent Acquisition and Skill Development
The success of a Project Management Office (PMO) depends on the skills and expertise of its personnel. This section outlines the key considerations when outlining the skills required for PMO personnel in federal agencies, recruiting and training a specialized PMO team, and building a culture of project management excellence within the agency.

Outlining the skills required
PMO personnel in federal agencies need a combination of technical and soft skills. They must have a strong understanding of project management principles, methodologies, and tools. They must also be able to lead and motivate teams, manage stakeholders, and communicate effectively with all levels of the organization.
The ideal candidate must be able to analyze data, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions. They must also have a strong understanding of the technical aspects of the projects they are managing. Finally, PMO personnel must be able to build relationships, collaborate with others, and resolve conflicts.
Strategies for recruiting and training
Recruiting and training a technical PMO team requires a strategic approach. Federal agencies can develop a clear job description outlining the role’s key responsibilities, required skills, and qualifications.
They can leverage social media platforms to promote job openings and engage with potential candidates. Finally, they can provide training and development opportunities to help PMO personnel develop their skills and expertise.
Building a culture of project management excellence
Creating a culture of project management excellence within the agency is critical for the success of the PMO. Federal agencies can establish a project management framework that provides a structured approach to managing projects and ensures that all projects are delivered following the relevant regulations and standards.
They can also provide ongoing training and development opportunities to help employees develop their project management skills. Finally, they can encourage collaboration and communication by providing tools and resources to facilitate cooperation between team members.
PMO Implementation and Change Management

Streamlining Rollout
Implementing a PMO in a federal agency demands strategic yet flexible planning. It starts with a clear, concise implementation plan closely aligned with the agency’s goals. Garnering leadership support is crucial as it lends authority and secures resources. Effective, transparent communication with stakeholders is vital to build trust and clarify the PMO’s role and benefits.
Customizing the PMO to fit the agency’s culture and objectives is critical. A pilot project can help test and refine the PMO’s processes before a full-scale rollout. This approach allows for adjustments based on real-world feedback, ensuring a smoother transition.
Facilitating Change and Adoption
Change management is integral to PMO adoption. Articulating the PMO’s vision and benefits helps align stakeholders with the new initiative. Involving them in decision-making can increase buy-in and reduce resistance. Addressing concerns proactively and celebrating small wins can bolster morale and demonstrate the PMO’s positive impact.
Overcoming Resistance
Understanding and addressing the root causes of resistance is essential. Effective communication, tailored to address specific concerns, can alleviate apprehensions. Leveraging internal change advocates can help smooth the transition by relating the PMO’s benefits in a context familiar to the staff. Training and support ensure that everyone adapts to the new system. Flexibility in response to feedback allows for continual refinement of the PMO implementation process.
In summary, successfully introducing a PMO in a federal agency involves thoughtful planning, inclusive change management, and a responsive approach to feedback and resistance. The PMO can effectively enhance the agency’s project management efficiency by focusing on these elements.
Measurement, Evaluation, and Continuous Improvement
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

Tailoring KPIs for Federal Projects
Selecting the right Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is crucial for a PMO in a federal setting. These KPIs should address federal project management aspects like compliance, budget adherence, and timely project delivery. They should also measure efficiency and stakeholder satisfaction, ensuring that the PMO’s performance aligns with the unique requirements of federal projects.
Assessing PMO Effectiveness
Evaluating a PMO’s effectiveness involves more than tracking KPIs. It requires a comprehensive review of how well the PMO meets its defined objectives and contributes to the agency’s overall goals. This can include assessing improvements in project delivery times, budget accuracy, and the quality of outcomes. Regular audits and reviews can provide insights into areas that are performing well and those that need improvement.
Fostering Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is vital to maintaining the PMO’s relevance and effectiveness. Implementing a feedback loop where project managers, team members, and stakeholders can provide input is critical. This feedback should be regularly reviewed to inform changes in the PMO’s processes and strategies. Encouraging an environment of open communication and learning ensures that the PMO remains adaptable and responsive to the evolving needs of the agency.
In summary, effectively measuring and evaluating a PMO in a federal agency involves setting relevant KPIs, regularly assessing its impact, and maintaining a feedback loop for continuous improvement. This approach helps ensure the PMO remains effective, efficient, and aligned with the agency’s evolving needs.
Harnessing the Power of a PMO in Federal Agencies
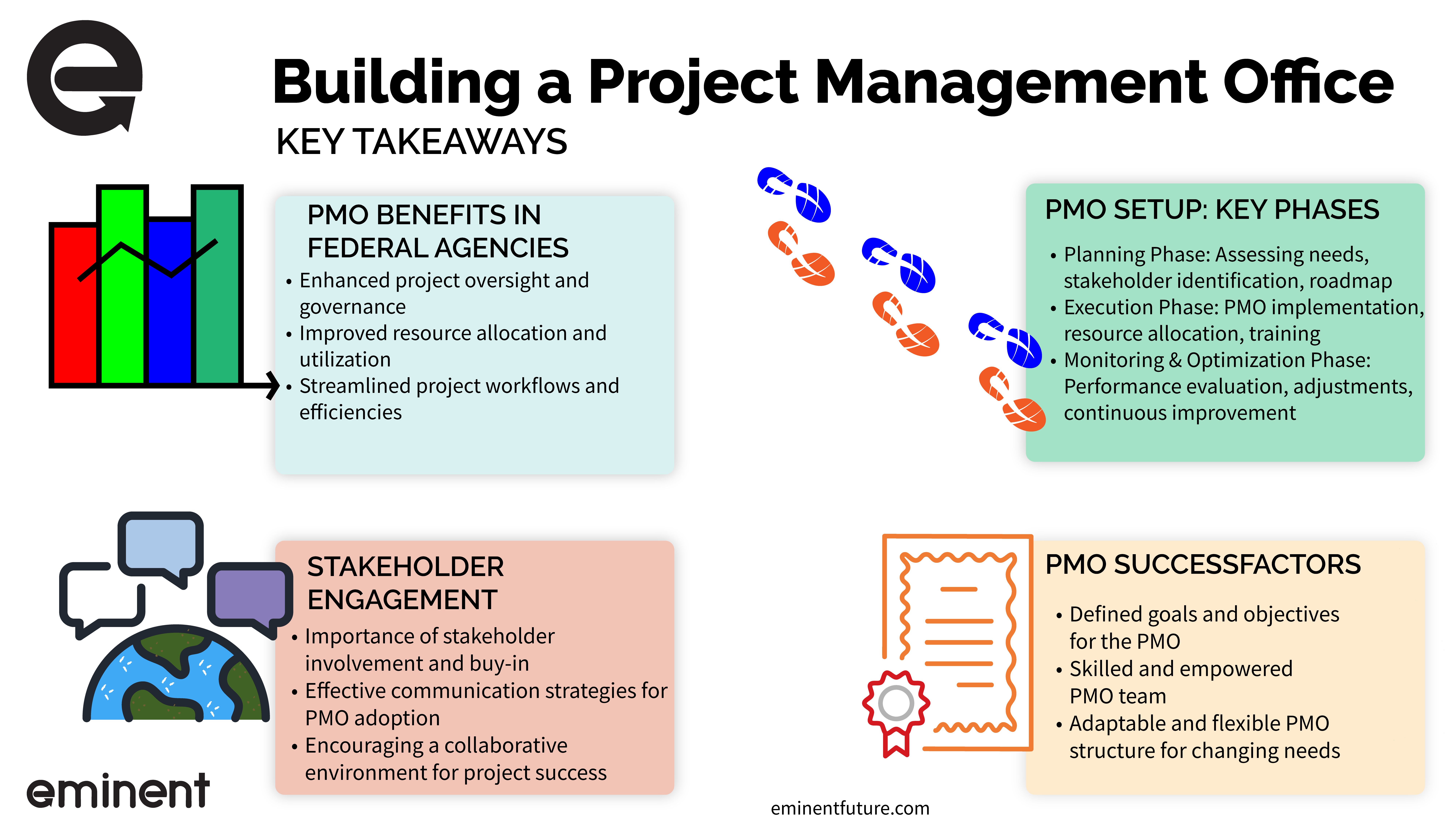
In sum, establishing a Project Management Office (PMO) within federal agencies is a significant step toward enhancing project management’s efficiency, transparency, and effectiveness. The guide provided here outlines a comprehensive journey from the planning phase to the continuous improvement of a PMO, tailored specifically for the unique environment of federal agencies.
A well-implemented PMO serves as a strategic asset, ensuring compliance and alignment with regulations and fostering a culture of excellence in project management. Federal agencies can build a PMO that genuinely resonates with their specific needs and challenges by adapting industry-standard frameworks, integrating suitable tools and technologies, and focusing on talent acquisition and skill development.
The implementation and change management process highlighted the importance of a strategic rollout, engaging leadership, and effectively managing change. Overcoming resistance and ensuring buy-in are critical to seamlessly integrating the PMO into the agency’s fabric.
Moreover, the PMO’s ongoing measuring, evaluating, and continuous improvement underscores its dynamic nature. Setting relevant KPIs, regularly assessing the PMO’s impact, and fostering an environment of open feedback and adaptation are crucial for its long-term success.
As federal agencies navigate complex and evolving landscapes, the PMO is a beacon of structured governance and management excellence. Its ability to adapt, grow, and improve ensures the success of individual projects. It contributes significantly to the broader mission and objectives of the agency.
Ultimately, the journey of establishing and nurturing a PMO is ongoing. It invests in future readiness, ensuring that federal agencies are equipped to meet today’s and tomorrow’s challenges with agility, precision, and a commitment to excellence.



